Variables in Java
I. What is variable in Java?
A variable is nothing but a name given to a storage area that our programs can manipulate..Each variable has a specific type. Data type determines size and layout of the variable's memory
II. Declaring a variable
type variable_name = value;
Ex:
int a, b, c;
int d = 35, e, f = 55;
byte z = 22; // initializes z.
double pi = 3.14159; // declares an approximation of pi.
char x = 'x'; // the variable x has the value 'x'.
String name = "Your name";\
III. Type of variables
1. Local Variables
.A variable declared inside the body of the method is called local variable. You can use this variable only within that method and the other methods in the class do not know that the variable exists.
A local variable cannot be defined with "static" keyword.
public class LocalVariableExample {
public int sum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum = sum + i;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalVariableExample localVariableExample = new LocalVariableExample();
int sum = localVariableExample.sum(10);
System.out.println("Sum of first 10 numbers -> " + sum);
}
}
Output:
Sum of first 10 numbers -> 45
2. Instance Variables (Non-Static Fields)- Declared in class but outside methods, constructor or block code
- Be created when an object is created. Then this variable is destroyed when that object is destroyed
– có thể được khai báo trong lớp trước hoặc sau khi sử dụng nó.
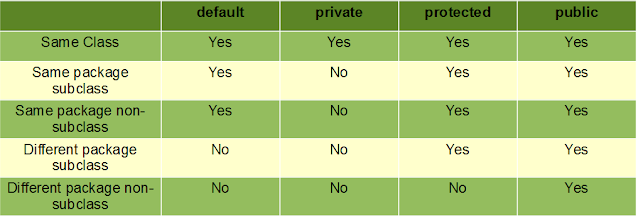
– Use access modifier for instance variables. If we do not specify any access specifier, then the default access modifier will be used.
– thông thường thì local variable sẽ visible với tất cả các method, constructor và block trong class.
– Have Initialization value . number is 0, boolean is false, object is null.
public class InstanceVariableExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
// Before assigning values to employee object
System.out.println(employee.empName);
System.out.println(employee.id);
System.out.println(employee.age);
employee.empName = "Ramesh";
employee.id = 100;
employee.age = 28;
// After assigning values to employee object
System.out.println(employee.empName);
System.out.println(employee.id);
System.out.println(employee.age);
}
}
class Employee {
// instance variable employee id
public int id;
// instance variable employee name
public String empName;
// instance variable employee age
public int age;
} Output:
null
0
0
Ramesh
100
28
3. Static variable
A variable that is declared as static is called a static variable
class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
private static String college = "ABC"; // static variable
public Student(int rollNo, String name) {
super();
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [rollNo=" + rollNo + ", name=" + name + ", college=" + college + "]";
}
}




.png)



